Order of the British Empire
| Most Excellent Order of the British Empire | |
|---|---|
 CBE neck decoration (in civil division) | |
| Awarded by the monarch of the United Kingdom | |
| Type | Order of chivalry |
| Established | 1917 |
| Motto | For God and the Empire |
| Eligibility | British nationals, citizens of the Commonwealth realms, or anyone who has made a significant achievement for the United Kingdom |
| Awarded for | Prominent national or regional achievements[1] |
| Status | Currently constituted |
| Sovereign | Charles III |
| Grand Master | Queen Camilla |
| Grades |
|
| Former grades | |
| Precedence | |
| Next (higher) | Royal Victorian Order |
| Next (lower) | Varies, depending on rank |
Military ribbon Civil ribbon | |
The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire is a British order of chivalry, rewarding contributions to the arts and sciences, work with charitable and welfare organizations, and public service outside the civil service.[2] It comprises five classes of award across both civil and military divisions, the most senior two of which make the recipient either a knight if male or a dame if female.[3] There is also the related British Empire Medal, whose recipients are affiliated with, but not members of, the order.
The order was established on 4 June 1917 by King George V, who created the order to recognise 'such persons, male or female, as may have rendered or shall hereafter render important services to Our Empire'.[3] Equal recognition was to be given for services rendered in the UK and overseas.[4] Today the majority of recipients are UK citizens, though a number of Commonwealth realms outside the UK continue to make appointments to the order.[5] Honorary awards may be made to citizens of other countries (where the Sovereign of the order is not the head of state).
Current classes
[edit]The five classes of appointment to the Order are, from highest grade to lowest grade:
- Knight Grand Cross or Dame Grand Cross of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (GBE)[a]
- Knight Commander or Dame Commander of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (KBE or DBE)
- Commander of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (CBE)
- Officer of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (OBE)
- Member of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (MBE)
The senior two ranks of Knight or Dame Grand Cross, and Knight or Dame Commander, entitle their members to use the title of Sir for men or Dame for women before their forename.
History
[edit]King George V founded the order to fill gaps in the British honours system:[citation needed]
- The Orders of the Garter, the Thistle and St Patrick honoured royals, peers, statesmen and eminent military commanders;
- The Order of the Bath honoured senior military officers and civil servants;
- The Order of St Michael and St George honoured diplomats and colonial officials;
- The Order of the Star of India and the Order of the Indian Empire honoured Indian rulers and British and Indian officials of the British Indian Empire; and
- The Royal Victorian Order, in the personal gift of the monarch, honoured those who had personally served the royal family.
In particular, George V wished to create an order to honour the many thousands of individuals from across the Empire who had served in a variety of non-combat roles during the First World War.[2]
From its foundation the order consisted of five classes (GBE, KBE/DBE, CBE, OBE and MBE) and was open to both women and men; provision was also made for conferring honorary awards on foreign recipients.[3] At the same time, alongside the order, the Medal of the Order of the British Empire was instituted, to serve as a lower award granting recipients affiliation but not membership. The first investiture took place at Ibrox Stadium, as part of a royal visit to the Glasgow shipyards, with awards of a GBE to Lord Strathclyde (in recognition of his role as chairman of the Scottish War Savings Committee) and the medal of the order to Lizzie Robinson, a munitions worker.[6]

The order had been established primarily as a civilian award; in August 1918, however (not long after its foundation) a number of awards were made to serving naval and military personnel. Four months later, a 'Military Division' was added to the order, to which serving personnel would in future be appointed.[7] The classes were the same as for the Civil Division (as it was now termed), but military awards were distinguished by the addition of a central vertical red stripe to the purple medal ribbon of the civil awards. In 1920 an MBE was awarded 'for an act of gallantry' for the first time, to Sydney Frank Blanck Esq, who had rescued an injured man from a burning building containing explosives.[6]
In December 1922 the statutes of the order were amended; there having been a large number of awards for war work prior to this date, these amended statutes placed the order on more of a peacetime footing.[4] For the first time numbers of appointments were limited, with the stipulation that senior awards in the Civil Division were to outnumber those in the Military Division by a proportion of six to one.[8] Furthermore appointments in the civil division were to be divided equally between UK and overseas awards. In terms of the Medal of the Order (but not the order itself), a distinction was made between awards 'for gallantry' and awards 'for meritorious service' (each being appropriately inscribed, and the former having laurel leaves decorating the clasp, the latter oak leaves).[8]
In 1933 the maximum number of appointments was increased. At this time holders of the medal 'for gallantry' (which had come to be known as the Empire Gallantry Medal) were given permission to use the postnominal letters EGM (and at the same time to add a laurel branch emblem to the ribbon of the medal); however in 1940 awards of the EGM ceased and all holders of the medal were instructed to exchange it for a new and more prestigious gallantry award: the George Cross.[9] In 1941, the medal of the order 'for meritorious service' was renamed the British Empire Medal, and the following year its recipients were granted the right to use the postnominal letters BEM.[4] During the war, the BEM came to be used to recognise acts of bravery which did not merit the award of a George Cross or George Medal,[9] a use which continued until the introduction of the Queen's Gallantry Medal in 1974.

The designs of insignia of the order were altered in 1937, prior to the coronation of King George VI, 'in commemoration of the reign of King George V and Queen Mary, during which the Order was founded'.[4] The figure of Britannia at the centre of the badge was replaced with an image of the crowned heads of the late King and Queen Mary, and the words 'Instituted by King George V' were added to the reverse of the badge. The colour of the riband was also changed: twenty years earlier, prior to the order's establishment, Queen Mary had made it known that pink would be her preferred colour for the riband of the proposed new order; but in the event purple was chosen.[10] Following her appointment as Grand Master of the order in 1936 a change was duly made and since 9 March 1937 the riband of the order has been 'rose pink edged with pearl grey’ (with the addition of a vertical pearl grey stripe in the centre for awards in the military division).[4]
During the Second World War, as had been the case during and after World War I, the number of military awards was greatly increased; between 1939 and 1946 there were over 33,000 appointments to the Military Division of the order from the UK and across the Empire.[9] Recommendations for all appointments to the Order of the British Empire were originally made on the nomination of the King's United Kingdom ministers, but in the early 1940s the system was changed to enable the governments of overseas dominions to make their own nominations; Canada and South Africa began doing so in 1942, followed later by Australia, New Zealand and other Commonwealth realms.[9]
In May 1957, forty years after the foundation of the order, it was announced that St Paul's Cathedral was to serve as the church of the order, and in 1960 a chapel was dedicated for its use within the crypt of the cathedral.[9]
In 1993 the British Empire Medal stopped being awarded by the United Kingdom as part of that year's reforms to the honours system; but awards resumed in 2012, starting with 293 BEMs awarded for Queen Elizabeth II's Diamond Jubilee.[11] In addition, the BEM is awarded by the Cook Islands and by some other Commonwealth nations.
In 2004, a report entitled A Matter of Honour: Reforming Our Honours System by a Commons select committee recommended phasing out the Order of the British Empire, as its title was "now considered to be unacceptable, being thought to embody values that are no longer shared by many of the country's population".[12] The committee further suggested changing the name of the award to the Order of British Excellence, and changing the rank of Commander to Companion (as the former was said to have a "militaristic ring"), as well as advocating for the abolition of knighthoods and damehoods;[13][14] the government, however, was not of the opinion that a case for change had been made, and the aforementioned suggestions and recommendations were not therefore pursued.[15]
In 2017 the centenary of the order was celebrated with a service at St Paul's Cathedral.[15]
Composition
[edit]The order is limited to 300 Knights and Dames Grand Cross, 845 Knights and Dames Commander, and 8,960 Commanders. There are no limits applied to the total number of members of the fourth and fifth classes, but no more than 858 officers and 1,464 members may be appointed per year. Foreign appointees, as honorary members, do not contribute to the numbers restricted to the order as full members do. Although the Order of the British Empire has by far the highest number of members of the British orders of chivalry, with over 100,000 living members worldwide, there are fewer appointments to knighthoods than in other orders.[2]
The British sovereign is the Sovereign of the order and appoints all other officers of the order (by convention, on the advice of the governments of the United Kingdom and some Commonwealth realms). The second-most senior officer is the Grand Master (a 'Prince of the Blood Royal, or other exalted personage' appointed by the Sovereign, who, by virtue of their appointment, becomes 'the First or Principal Knight Grand Cross of the same Order').[3] The position of Grand Master has been held by the following people:
| No. | Portrait | Name (Born–died) |
Term of office | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Took office | Left office | |||
| 1 |  |
Edward, Prince of Wales (1894–1972) |
4 June 1917 | 20 January 1936 |
| 2 |  |
Queen Mary (1865–1953) |
27 March 1936 | 24 March 1953 |
| 3 |  |
The Duke of Edinburgh (1921–2021) |
1 June 1953 | 9 April 2021 |
| 4 |  |
Queen Camilla (1947–present) |
23 April 2024 | present |
Though men can be knighted separately from an order of chivalry (Knight Bachelor), women cannot, and so the rank of Knight/Dame Commander of the Order is the lowest rank of damehood, and second-lowest of knighthood (above Knights Bachelor). Because of this, an appointment as Dame Commander is made in circumstances in which a man would be created a Knight Bachelor. For example, by convention, female judges of the High Court of Justice are created Dames Commander after appointment, while male judges become Knights Bachelor.
From time to time, individuals may be promoted to a higher grade within the Order, thereby ceasing usage of the junior post-nominal letters.
Officers
[edit]In addition to the sovereign and the grand master, the order has six further officers:[16]
- Prelate: Bishop of London, The Rt Hon. & Rt Rev. Dame Sarah Mullaly DBE[17]
- Dean: Dean of St Paul's (ex officio), The Very Rev. Andrew Tremlett
- Secretary: Secretary of the Central Chancery of the Orders of Knighthood, Lieutenant Colonel Stephen Segrave
- Registrar: Secretary of the Cabinet and Head of the Home Civil Service, Simon Case CVO
- King of Arms: Lieutenant General Sir Simon Mayall KBE CB[18]
- Lady Usher of the Purple Rod: Dame Amelia Fawcett DBE CVO
At its foundation the order was served by three officers: the King of Arms, the Registrar & Secretary and the Gentleman Usher of the Purple Rod. In 1922 the Prelate was added, and the office of Registrar was separated from that of Secretary: the former was to be responsible for recording all proceedings connected with the order, issuing warrants under the seal of the order and making arrangements for investitures; while the latter (at that time the Permanent Secretary to the Treasury) was responsible for collecting and tabulating the names of those who were to receive an award.[8] The office of Dean was added in 1957.[9]
The King of Arms is not a member of the College of Arms, as are many other heraldic officers; and the Lady Usher of the Purple Rod does not – unlike the Order of the Garter equivalent, the Lady Usher of the Black Rod – perform any duties related to the House of Lords.
Commonwealth awards
[edit]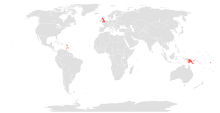
Since the Second World War, several Commonwealth realms have established their own national system of honours and awards and have created their own unique orders, decorations and medals. A number, though, continue to make recommendations for appointments to the Order of the British Empire. In 2024 appointments to the order were made by the governments of:[19]
- Antigua and Barbuda
- The Bahamas
- Belize
- Grenada
- Papua New Guinea
- Saint Christopher and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Solomon Islands
and the New Zealand associated state of the Cook Islands.
Canada seldom made recommendations for appointments to the Order of the British Empire except for the Second World War and Korea but continued to recommend gallantry awards for both military and civilians until the creation of the Order of Canada.[20] Australian recommendations for the Order of the British Empire continued to be submitted for 15 years after the creation of the Order of Australia. The last Australian Federal recommendations were for the 1983 New Year honours and the last Australian state recommendations were for the 1989 Queen's Birthday honours.[21] The New Zealand Government ceased to recommend the Order in 1996, upon the establishment of the New Zealand Order of Merit, but the Government of the Cook Islands continues to do so.[22]
Honorary awards
[edit]Most members of the order are citizens of the United Kingdom or Commonwealth realms that use the UK system of honours and awards. In addition, honorary awards may be made to citizens of nations where the monarch is not head of state; these permit use of post-nominal letters, but not the title of Sir or Dame. Honorary appointees who later become a citizen of a Commonwealth realm can convert their appointment from honorary to substantive, and they then enjoy all privileges of membership of the order, including use of the title of Sir and Dame for the senior two ranks of the Order. (An example of the latter is Irish broadcaster Terry Wogan, who was appointed an honorary Knight Commander of the Order in 2005, and on successful application for British citizenship, held alongside his Irish citizenship, was made a substantive member and subsequently styled as Sir Terry Wogan).[23][24]
Gallantry awards
[edit]
Although initially intended to recognise meritorious service, the order began to also be awarded for gallantry. There were an increased number of cases in the Second World War for service personnel and civilians including the merchant navy, police, emergency services and civil defence, mostly MBEs but with a small number of OBEs and CBEs. Such awards were for gallantry that did not reach the standard of the George Medal (even though, as appointments to an order of chivalry, they were listed before it on the Order of Wear. In contrast to awards for meritorious service, which usually appear without a citation, there were often citations for gallantry awards, some detailed and graphic.[25] From 14 January 1958, these awards were designated Commander, Officer or Member of the Order of the British Empire for Gallantry.[26]
Any individual made a member of the order for gallantry after 14 January 1958 wears an emblem of two crossed silver oak leaves on the same ribbon as the badge, with a miniature version on the ribbon bar when worn alone. When the ribbon only is worn the emblem is worn in miniature.[26] It could not be awarded posthumously, and was replaced in 1974 with the Queen's Gallantry Medal (QGM). If recipients of the Order of the British Empire for Gallantry received promotion within the order, whether for gallantry or otherwise, they continued to wear also the insignia of the lower grade with the oak leaves;[27] however, they used only the post-nominal letters of the higher grade.
Insignia
[edit]- Badges and ribands of the Order of the British Empire (1937-present)
-
Obverse (left) and reverse of the MBE badge and riband (civil division)
-
MBE badge as awarded to a female recipient (civil division)
-
OBE badge and riband (military division)
-
CBE badge and riband (military division)
When the order was founded in 1917, badges, ribands and stars were appointed for wear by recipients. In 1929 mantles, hats and collars were added for recipients of the highest class of the order (GBE). The designs of all these items underwent major changes in 1937.[10]
Badge
[edit]The badge is worn by all members of the order; the size, colour and design depends on the class of award. The badge is in the form of a cross patonce (having the arms growing broader and floriated toward the end), the obverse of which bears the same field as the star (that is, either Britannia or, since 1937, George V and Queen Mary); the reverse bears George V's Royal and Imperial Cypher. Both are within a ring bearing the motto of the Order. The size of the badges varies according to rank: the higher classes have slightly larger badges. The badges of Knights and Dames Grand Cross, Knights and Dames Commander, and commanders are enamelled with pale blue crosses and crimson rings; those of officers are plain silver-gilt; those of members are plain silver.
Riband
[edit]From 1917 until 1937, the badge of the order was suspended on a purple ribbon, with a red central stripe being added for the military division in 1918. Since 1937, the ribbon has been rose-pink with pearl-grey edges (with the addition of a pearl-grey central stripe for the military division). Knights and Dames Grand Cross wear it on a broad riband or sash, passing from the right shoulder to the left hip. Knights Commander and male Commanders wear the badge from a ribbon around the neck; male Officers and Members wear the badge from a ribbon on the left chest; female recipients other than Dames Grand Cross (unless in military uniform) normally wear it from a bow on the left shoulder.
Star
[edit]An eight-pointed star is worn, pinned to the left breast, by Knights/Dames Grand Cross and Knights/Dames Commander; it is not worn by the more junior classes. Varying in size depending on class, it bears a crimson ring with the motto of the order inscribed. Within the ring, a figure of Britannia was originally shown; but since 1937 the effigies of George V and Mary of Teck have been shown instead.
- Badges and ribands of the Order of the British Empire (1917-1937)
-
MBE badge as awarded to a female recipient (civil division)
-
MBE badge and riband (military division)
-
OBE badge and riband (military division)
-
KBE badge, riband and star (military division)
Mantles and collars
[edit]In 1929, to bring the order into line with the other orders of chivalry, members of the first class of the order (GBE) were provided with mantles and collars.[4] Only Knights and Dames Grand Cross wear these elaborate vestments:
- The mantle is a cloak-like garment of rose pink satin lined with pearl-grey silk (prior to 1937 it was of purple satin). On the left side is a representation of the star of the order (as pictured below).
- Initially a purple hat was also provided to be worn with the mantle; in 1937 the colour was changed to black (though it is now rarely, if ever, worn).[10]
- The collar is made of gold. It consists of six medallions depicting the Royal Arms, alternating with six medallions depicting the Royal and Imperial Cypher of George V (GRI, which stands for "Georgius Rex Imperator"). The medallions are linked with gold cables depicting lions and crowns. When collars are worn the badge is suspended from the collar.
Use of the mantle is limited to important occasions (such as quadrennial services and coronations); the mantle is always worn with the collar. Although the mantle was introduced in 1929, very few mantles would have been produced prior to the 1937 design changes, as there were few occasions for wearing them in the intervening years.[10]
On certain days designated by the Sovereign, known as "collar days", members attending formal events may wear the order's collar over their military uniform, formal day dress, evening wear or robes of office.
Collars are returned upon the death of their owners, but other insignia may be retained.
The six office-holders of the order wear pearl-grey mantles lined with rose-pink, having on the right side a purple shield charged with the roundel from the badge.[28] Each of these office-holders wears a unique badge of office, suspended from a gold chain worn around the neck.
- Knight and Dame Grand Cross insignia
-
Mantle worn by Knights and Dames Grand Cross (GBE)
-
Close-up of the Star on the mantle
-
Collar, badge and Star of a Knight or Dame Grand Cross of the Order
-
Broad riband and badge of a Knight Grand Cross of the Order
The British Empire Medal is made of silver. On the obverse is an image of Britannia surrounded by the motto, with the words "For Meritorious Service" at the bottom; on the reverse is George V's Imperial and Royal Cypher, with the words "Instituted by King George V" at the bottom. The name of the recipient is engraved on the rim. This medal is nicknamed "the Gong",[citation needed] and comes in both a full-sized and miniature versions – the latter for formal white-tie and informal black-tie occasions.
A lapel pin for everyday wear was first announced at the end of December 2006, and is available to recipients of all levels of the order, as well as to holders of the British Empire Medal. The pin design is not unique to any level. The pin features the badge of the order, enclosed in a circle of ribbon of its colours of pink and grey. Lapel pins must be purchased separately by a member of the order.[29] The creation of such a pin was recommended in Sir Hayden Phillips' review of the honours system in 2004.[30]
| Civil | Military | |
|---|---|---|
| 1917–1935 | ||
| Since 1936 |
Chapel
[edit]
The Chapel of the Order of the British Empire is in St Paul's Cathedral. It occupies the far eastern end of the cathedral crypt and was dedicated in 1960. The only heraldic banners normally on display in the chapel are those of the Sovereign of the Order of the British Empire and of the Grand Master of the Order of the British Empire. Rather than using this chapel, the Order now holds its great services upstairs in the nave of the cathedral. In addition to the Chapel of the Order of the British Empire, St Paul's Cathedral also houses the Chapel of The Most Distinguished Order of St Michael and St George. Religious services for the whole Order are held every four years; new Knights and Dames Grand Cross are installed at these services.
Precedence and privileges
[edit]
Knights Grand Cross and Knights Commander prefix Sir, and Dames Grand Cross and Dames Commander prefix Dame, to their forenames.[b] Wives of Knights may prefix Lady to their surnames, but no equivalent privilege exists for husbands of Knights or spouses of Dames. Such forms are not used by peers and princes, except when the names of the former are written out in their fullest forms. Male clergy of the Church of England or the Church of Scotland do not use the title Sir (unless they were knighted before being ordained) as they do not receive the accolade (they are not dubbed "knight" with a sword), although they do append the post-nominal letters; dames do not receive the accolade, and therefore female clergy are free to use the title Dame.
Knights and Dames Grand Cross use the post-nominal GBE; Knights Commander, KBE; Dames Commander, DBE; Commanders, CBE; Officers, OBE; and Members, MBE. The post-nominal for the British Empire Medal is BEM.
Members of all classes of the order are assigned positions in the order of precedence. Wives of male members of all classes also feature on the order of precedence, as do sons, daughters and daughters-in-law of Knights Grand Cross and Knights Commander; relatives of Ladies of the Order, however, are not assigned any special precedence. As a general rule, only wives and children of male recipients are afforded privileges.
Knights and Dames Grand Cross are also entitled to be granted heraldic supporters. They may, furthermore, encircle their arms with a depiction of the circlet (a circle bearing the motto) and the collar; the former is shown either outside or on top of the latter. Knights and Dames Commander and Commanders may display the circlet, but not the collar, surrounding their arms. The badge is depicted suspended from the collar or circlet.[31]
Current knights and dames grand cross
[edit]
- Sovereign: King Charles III
- Grand Master: Queen Camilla (2024)
Substantive
[edit]Military ranks listed denotes the awarded being in the military division.
Honorary
[edit]An honorary Order of the British Empire award can be given to a non-British citizen for their work in a chosen field.
Forfeiture
[edit]Only the monarch can annul an honour. The Honours Forfeiture Committee considers cases and makes recommendations for forfeiture. An individual can renounce their honour by returning the insignia to Buckingham Palace and by ceasing to make reference to their honour, but they still hold the honour unless and until annulled by the monarch.[32]
People who declined Order of the British Empire honours
[edit]In 2003, The Sunday Times published a list of the people who had rejected the Order of the British Empire, including David Bowie, John Cleese, Nigella Lawson, Elgar Howarth, L. S. Lowry, George Melly, and J. G. Ballard.[33] In addition, Ballard voiced his opposition to the honours system, calling it "a preposterous charade".[33]
The order has attracted some criticism for its naming having connection with the idea of the now-extinct British Empire.[34] Benjamin Zephaniah, a British poet of Jamaican and Barbadian descent, publicly rejected appointment as an Officer in 2003 because, he asserted, it reminded him of "thousands of years of brutality". He also said that "it reminds me of how my foremothers were raped and my forefathers brutalised".[35]
The author C. S. Lewis (1898–1963) was named on the last list of honours by George VI in December 1951. Despite being a monarchist, he declined so as to avoid association with any political issues.[36][37]
In 2019, John Oliver turned down an offer of an OBE, which would have been part of the Queen's New Year's Honours list.[38][39]
The Beatles were appointed Members in 1965: John Lennon justified his investiture by comparing military membership in the Order: "Lots of people who complained about us receiving the MBE [status] received theirs for heroism in the war – for killing people ... We received ours for entertaining other people. I'd say we deserve ours more". Lennon later returned his MBE insignia on 25 November 1969, as part of his ongoing peace protests.[40] Other criticism centres on the view that many recipients of the Order are being rewarded with honours for simply doing their jobs; critics say that the Civil Service and Judiciary receive far more orders and honours than leaders of other professions.[34]
Chin Peng, a veteran guerrilla fighter of the Malayan Peoples' Anti-Japanese Army, was appointed as an Officer for his role in fighting against the Japanese occupation of Malaya during World War II, in close co-operation with the British commando Force 136. Several years after WWII, his OBE membership was withdrawn by the British government (and became undesirable to Chin Peng himself) when the Communist leader headed his party's guerrilla insurgency against the British Empire during the Malayan Emergency.[41]
See also
[edit]- Orders, decorations, and medals of the United Kingdom – the British honours system
- List of knights grand cross of the Order of the British Empire
- List of dames grand cross of the Order of the British Empire
- List of honorary British knights and dames
- United Kingdom order of precedence
- Honours Committee
- Roger Willoughby, For God and the Empire. The Medal or the Order of the British Empire, 1917-1922 (Savannah Publications, London, 2012) ISBN 1 902366 53 0
Notes
[edit]- ^ It is commonly written without "of the Most Excellent Order" and other words not implied by the post-nominals.
- ^ Never surnames – thus Sir Antony Sher may be shortened to Sir Antony, but not to Sir Sher.
References
[edit]- ^ "Guide to the Honours". BBC News. BBC. 10 June 2015. Retrieved 25 May 2016.
- ^ a b c "Order of the British Empire". The Official Website of the British Monarchy. The Royal Household. Archived from the original on 27 March 2010. Retrieved 24 August 2009.
- ^ a b c d "No. 30250". The London Gazette (2nd supplement). 24 August 1917. pp. 8791–8999.
- ^ a b c d e f Malloch, Russell. "The Order of the British Empire (part two): 1922 to 1937". The Gazette. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ "Commonwealth New Year and Birthday Honours lists (1981-2024)". The Gazette. His Majesty's Stationery Office. Retrieved 7 August 2024.
- ^ a b Malloch, Russell. "The Order of the British Empire (part one): 1917 to 1922". The Gazette. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ "No. 31084". The London Gazette. 27 December 1918. p. 15135.
- ^ a b c "No. 32781". The London Gazette. 29 December 1922. p. 9157.
- ^ a b c d e f Malloch, Russell. "The Order of the British Empire (part three): 1937-1957". The Gazette. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ a b c d Galloway, Peter (1996). The Order of the British Empire. Central Chancery of the Orders of Knighthood. p. 12.
- ^ "Birthday Honours: 'Working class' British Empire Medal revived". BBC News. BBC. 16 June 2012. Retrieved 20 June 2012.
- ^ "A Matter of Honour: Reforming Our Honours System" (PDF). House of Commons Public Administration Select Committee. Parliament.uk. 13 July 2004. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- ^ "Select Committee on Public Administration Fifth Report".
- ^ "Honours system outdated, say MPs", BBC News, 13 July 2004, Retrieved 28 February 2007
- ^ a b Malloch, Russell. "The Order of the British Empire (part five): 1993-2017". The Gazette. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ "The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire : Newsletter" (PDF). The Central Chancery of the Orders of Knighthood. December 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 24 July 2019. Retrieved 23 April 2019.
- ^ HM Government (7 December 2018). "Central Chancery of the Orders of Knighthood". The London Gazette. Archived from the original on 10 April 2023. Retrieved 22 December 2018.
- ^ "No. 64397". The London Gazette. 15 May 2024. p. 9430.
- ^ "Commonwealth New Year and Birthday Honours lists (1981-2024)". London Gazette. Retrieved 25 May 2024.
- ^ However, there were awards of the related British Empire Medal for Gallantry, whose recipients are affiliated with, but not members of the Order of the British Empire, after the creation of the Order of Canada. see "No. 44630". The London Gazette. 9 July 1968. p. 7607.
- ^ London Gazette 51778, Sat, 17 June 1989, p. 45
- ^ New Zealand Royal Honours System: History, Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet, Retrieved on 19 May 2020
- ^ "No. 57855". The London Gazette (1st supplement). 31 December 2005. p. 26.
- ^ "Radio's Wogan becomes Sir Terry". BBC News. BBC. 6 December 2005. Retrieved 7 February 2009.
- ^ Abbott, PE; Tamplin, J. M. A. (1981). British Gallantry Awards. London: Nimrod Dix & Co. Chapters 35–38. ISBN 978-0-902633-74-2.
- ^ a b "No. 41285". The London Gazette (Supplement). 14 January 1958. p. 365.
- ^ "No. 56878". The London Gazette (Supplement). 17 March 2003. p. 3353.
- ^ "Queen marks 100 years of Order of the British Empire". City Matters. 2 June 2017. Retrieved 7 August 2024.
- ^ "Emblem for honours (Archived 4 April 2012)". The National Archives. DirectGov (UK). Archived from the original on 4 April 2012. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
- ^ "BEM Recipients Entitled to New Emblem". The Berwickshire News. 12 November 2008. Archived from the original on 29 July 2014. Retrieved 26 July 2014.
- ^ Statutes 1995, article 34.
- ^ "Having honours taken away (forfeiture)". GOV.UK. 30 September 2021. Retrieved 24 January 2024.
- ^ a b McGavin, Henry (22 December 2003). "Honoured? No thanks, say elite of arts and TV". Independent. Archived from the original on 24 May 2022. Retrieved 4 March 2018.
- ^ a b A reformed Honours system, Select Committee on Public Administration, 7 July 2004, Retrieved 13 May 2012
- ^ Mills, Merope (27 November 2003). "Rasta poet publicly rejects his OBE". The Guardian. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- ^ "Chronology of the Life of C. S. Lewis". Archived from the original on 6 February 2012.
- ^ Lewis, C. S. (1994). W. H. Lewis, Walter Hooper (ed.). Letters of C. S. Lewis. New York: Mariner Books. p. 528. ISBN 978-0-15-650871-1.
- ^ Conan O'Brien (21 October 2019). "Conan O'Brien Needs a Friend – John Oliver Episode 42". TeamCoco.com (Podcast). Team Coco. Event occurs at 52:35. Retrieved 5 October 2022.
- ^ Nunn, Christina (21 January 2021). "John Oliver Rejected Queen Elizabeth's Royal Award — 'Why on Earth Would I Want That?'". Showbiz Cheat Sheet. Retrieved 5 October 2022.
- ^ Roylance, Brian; Harrison, George; Lennon, John; McCartney, Paul; Starr, Ringo (2000). The Beatles Anthology. Chronicle Books. pp. 183. ISBN 978-0-8118-2684-6.
- ^ Dead or Alive (subscription required) Archived 21 July 2013 at the Wayback Machine Time, 12 May 1952
Further reading
[edit]- Galloway, Peter (1996). The Order of the British Empire. Central Chancery of the Orders of Knighthood. ISBN 978-0-907605-65-2.
- Hood, Frederic (1967). The Chapel of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire. With a foreword by Prince Philip.
- Weatherly, Cecil (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 15 (11th ed.). London: Cambridge University Press. pp. 851–867.
- Statutes of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (PDF). London: The Central Chancery of the Orders of Knighthood. 1995. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 March 2023.
External links
[edit]- Order of the British Empire – official website of the British Monarchy
- The Honours system – UK Government
- Queen's Birthday and New Year honours – The London Gazette, lists recipients of honours
- "The Most Excellent Order of the British Empire" (2002) – Cambridge University Heraldic and Genealogical Society
- "Order of Precedence in England and Wales", Velde, F. R. (2003) – Heraldica.org
- Search recommendations for the Order of the British Empire on the UK National Archives' website
- The Chapel of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire – OBE Chapel Exterior detail – JPEG image, IanMcGrawPhotos.co.uk